The forest of chimpanzees
Budongo Forest
Geographical location & uniqueness
|
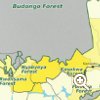
Budongo Forest, another semi-evergreen forest of the drier Guineo-Congolian type, is placed on the escarpment overlooking Lake Albert in western Uganda. Budongo CFR, managed by NFA, covers 82,530 ha. This includes Kitigo woodland in the north-west plus other non-forest areas. Therefore, 58% of the gazetted area has natural forest cover. In total the forest reserve is more than twice as large as Mabira CFR and more than three times as large as Kakamega Forest. It encompasses four nature reserves, the smallest being highly valued amongst scientists. Most of the much smaller forest reserves to the south do not have any natural forest cover any more today. Although selectively logged over the last 60 years, Budongo Forest shows a remarkable stability in forest cover and extent, this by avoiding clear-felling. One tree species (Cynometra) proofed to be too hard for the saws and therefore left parts of the forest with a forest type closer to near-primary forest than this is the case with the other here presented forests. The presence of Mahogany species renders it the largest and most valuable timber forest in Uganda. Nowadays Budongo Forest suffers most from pitsawing and hunting. Budongo CFR is placed on altitudes between 900 and 1,440 m a.s.l. and has an annual amount in rainfall of 1,200 to 1,800 mm. The water drains via the small rivers Waisoke, Waki and Sonso in north-westerly direction into Lake Albert. Budongo Forest is exceptionally rich in biodiversity with some endemic species. It is listed third in biodiversity importance for Uganda. Most famous it is for its well-studied chimpanzees, with primate research conducted from the Budongo Conservation Field Station next to a former sawmill in the middle of the forest. Among scientists Budongo Forest is also known for being the longest studied rainforest in East Africa. Read more about "Forest surrounding" and "Tourist attractions" on the second page. |
|
1 / 2 |


 Activities
Activities